Organisation : Bangladesh Computer Council
Facility Name : Bangladesh Computer Council Certifying Authority BCC-CA
Country : Bangladesh
Website : https://www.bcc-ca.gov.bd/
How to get BCC-CA Certificate?
To get BCC-CA Certificate, Follow the below steps
Related / Similar Status :

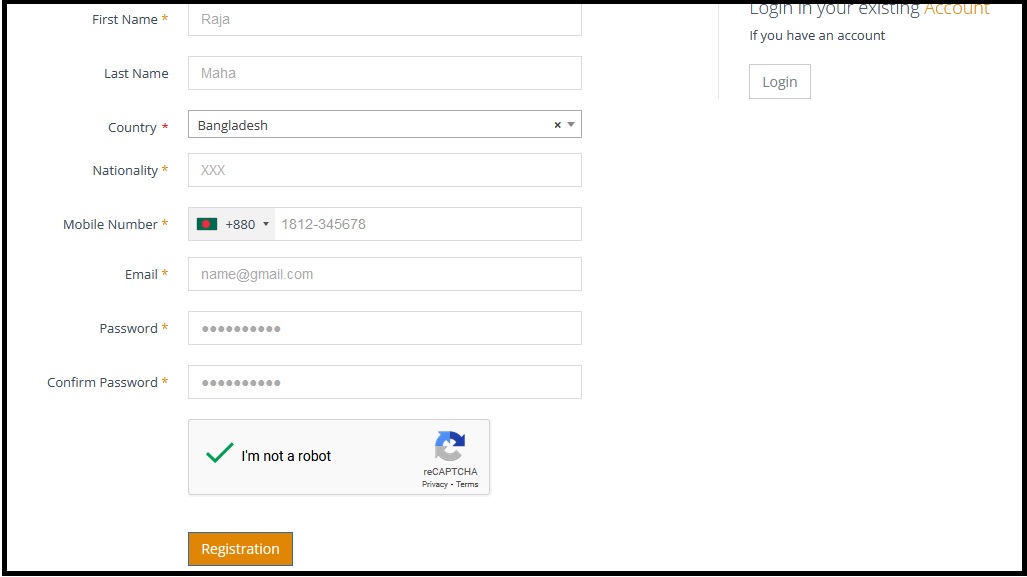
Step 1: Go to the link https://www.bcc-ca.gov.bd/register
Step 2: Enter your First Name
Step 3: Enter your Country
Step 4: Enter your Nationality
Step 5: Enter your Mobile Number
Step 6: Enter your Email
Step 7: Enter your Password
Step 8: Enter your Confirm Password
Step 9: After login in this portal user can enroll any type of certificate. Relevant documents are needed to enroll a certificate
Step 10: After enrollment user will generate private-public key in their local machine through our BCC-CA client application
Step 11: Finally, user will find download option after the CSR is signed by BCC-CA authority in the portal.

Bangladesh Computer Council Certifying Authority (BCC-CA)
1. Digital Certificate
BCCCA provides Class-1, Class-2 and Class-3 certificates for individual and organizations according to CCA guideline.
2. SSL Certificate
SSL is used to secure online transactions, data transfer and logins, and more recently is becoming the norm when securing browsing of social media sites.
3. Cryptographic Token
BCCCA Provides both individual and organizational certificates through USB security tokens.
About BCC
Bangladesh Computer Council CA certifying authority (BCC CA) is an only Government Certifying Authority (CA) under the Bangladesh Computer Council. It provides different types of technology oriented services like digital certificates; Web based SSL certificates and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) enablement tools in Bangladesh.
FAQ on Bangladesh Computer Council Certifying Authority (BCC-CA)
Frequently Asked Questions FAQ on Bangladesh Computer Council Certifying Authority (BCC-CA)
1. What is sender authentication?
It’s a process to ensure that a message does not originate from someone other than its purported sender. Sender authentication is achieved through two related mechanisms: digital signature and digital certificate.
2. What is encryption?
Encryption is the transformation of information from readable form into some unreadable form.
3. What is Digital Certificate?
Digital certificates are the digital equivalent (i.e. electronic format) of physical or paper certificates. Examples of physical certificates are driver’s licenses, passports or membership cards. Certificates serve as identity of an individual for a certain purpose, e.g. a driver’s license identifies someone who can legally drive in a particular country. Likewise, a digital certificate can be presented electronically to prove your identity or your right to access information or services on the Internet.
4. What is decryption?
Decryption is the reverse of encryption; it’s the transformation of encrypted data back into some intelligible form.
5. What is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)?
The Public key infrastructure (PKI) is the set of hardware, software, policies, processes, and procedures required to create, manage, distribute, use, store, and revoke digital certificates and public-keys.